Seborrheic Eczema Treatment
Eczema-Ltd III makes an excellent treatment for seborrheic eczema. Treatment varies, depending on the affected areas and the severity of the condition. Seborrheic Eczema can be treated with using a medicated shampoo and along with Eczema-Ltd III. You may want to compare your past treatment with our treatment. Head over to our home page to read more.
Washing your face or the affected area two or three times a day with a cleanser such as Neutrogena dry, sensitive skin cleansing bar can help control facial oiliness or Dove 'Sensitive Skin Unscented Beauty Bar'. The Dove company has been know for years to work very well. When Seborrheic eczema affects the scalp, you may find it necessary to shampoo daily with one of many non-prescription medicated shampoos.
Shampooing Tips for a Scalp with Seborrheic Eczema:
- Look for a shampoo that contains one of four important ingredients: coal tar, zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or salicylic acid.
- Shampoo as often as every day, or as occasionally as two to three times per week.
- Leave the shampoo on your hair and scalp for at least five minutes to make sure that the medication reaches the scalp.
Keeping the skin moisturizer will greatly help improve Seborrheic Eczema. There are some products on the market that will provide that proper moisturizer your skin needs. The first is jojoba oil. Jojoba oil can be found at GNC, Natural Health food store or online at The Jojoba Company
Treating Seborrheic eczema often requires patience - treatment can last many months until the scaling subsides. The condition can be kept under control so that the embarrassing scaling is minimized. It is not known whether emotional stress, diet or food allergies trigger the condition. To control it, a treatment program should be developed and followed.
Seborrheic Eczema Cause
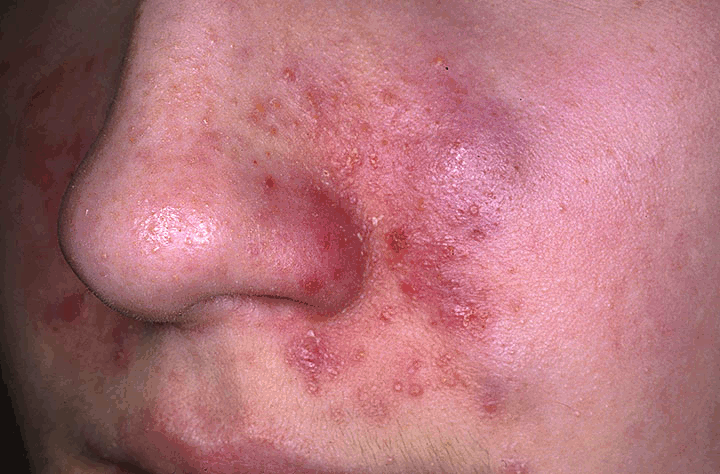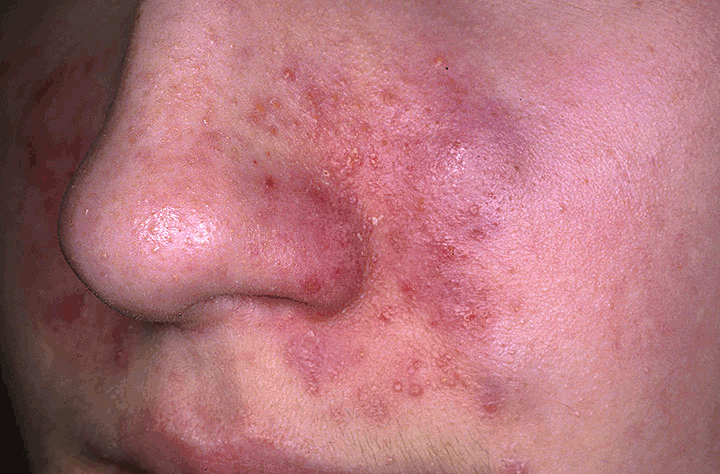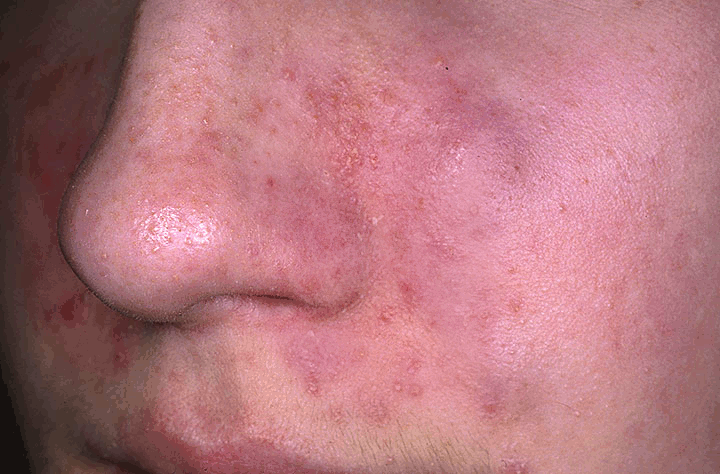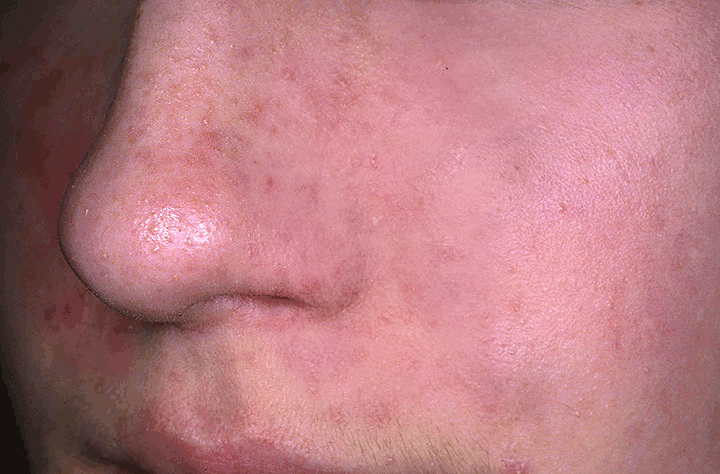
Yeast is the mostly like cause of Seborrheic eczema. One yeast group called Pityrosporum ovale could be the mostly likely skin irritant which is fairly common on all people even with normal skin. For those with over active sebacceous glands, the environment becomes healthy for the fungus to grow. Try to shampoo the hair and wash the skin more often.
Seborrheic dermatitis appears to run in families. Stress, weather extremes, oily skin, infrequent hair washing or skin cleaning, use of lotions that contain alcohol, or skin disorders such as acne or obesity may increase the risk. Neurological conditions, including Parkinson's disease, head injury, and stroke can also be associated with seborrheic dermatitis. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is also associated with a higher incidence of seborrheic eczema.
Occurrence of Seborrheic Eczema
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting areas of the head and trunk where sebaceous glands are most prominent. Adult seborrheic eczema is believed by some to be caused by Pityrosporum ovale a yeast condition. Scalp seborrhea varies from mild dandruff to dense, diffuse, adherent scales. Facial and trunk seborrhea is characterized by powdery or greasy scales in skin folds and along hair margins.
Adult seborrheic eczema also known as Dandruff or Seborrheic dermatitis. Cradle cap is the term used when seborrheic dermatitis affects the scalp of infants.
Seborrheic eczema is a patch of red irritated skin that itches constantly. The name of seborrheic is applicable to the sebacceous glands as extra oil is produced as the patient often has an auto-immune disorder and is hyper or in a state of 'fight or flight'. Often the body is dehydrated as a cause of the hyperness. Areas affected can be any portion of the body, but most often seborrheic eczema occurs in areas irritated by eye glasses over the bridge of the nose and behind the ear where the glass frames touch the ears. Likewise, the nose crevice with high oil production can be prone to having seborrheic eczema. Any skin folds can be affected where there is movement and that are areas of sebacceous glands. Also, the scalp if often affected and is often called dandruff.
Symptoms of Seborrheic Eczema
Symptoms of seborrheic eczema include:
- Raised skin lesions or 'bumps' that are uncomfortable and unattractive
- Oily scales over large areas that often reoccur called dandruff
- Scaly seborrheic eczema symptoms may appear at any location
- Skin infections may occur
- Redness may range from mild to severe
- Alopecia or hair loss may occur in some patients
Adult seborrheic eczema has the appearance of irritated scaling, red skin that is most often oily in nature to to the over active sebaceous glands. Seborrheic eczema is also known as dandruff. Seborrheic eczema usually causes the patient to itch severely. Try to avoid scratching.
Seborrheic eczema and seborrheic psoriasis are difficult to diagnose. Most often the patient will be diagnosed with seborrheic eczema if the red, patches of scales are on the scalp or on areas of skin with a high concentration of sebacceous glands with resulting oily scales. Seborrheic psoriasis will most often be found on areas of dry skin such as elbows and knees, etc.
Patients ages can vary extensively from infancy to older people. Children would have 'cradle cap' which clears often in a few days or weeks without treatment. Infantile seborrheic eczema could evolve into seborrheic eczema with the constant irritation of cleaning your child with 'over cleaning' with disposable tissues with alcohol, etc. that can break the skin down. Try a clean wet wash cloth with a mild soap such as Dove moisturizing bar soap.

